The Difference Between a Turbocharger and a Supercharger

Today, let's identify the difference between a turbocharger and a supercharger.
In the automotive world today, "Boost" is a frequently discussed topic. Both of these chargers are extremely important for increasing your engine's performance and obtaining more power and torque. Although both the turbocharger and supercharger work by forcing more air into the engine, the way they operate is completely different.
Let's understand the difference between these two simply and correctly.
Turbocharger
The turbocharger is what is used in most modern vehicles today. This is a highly efficient technology. Let's discuss how the turbocharger works.
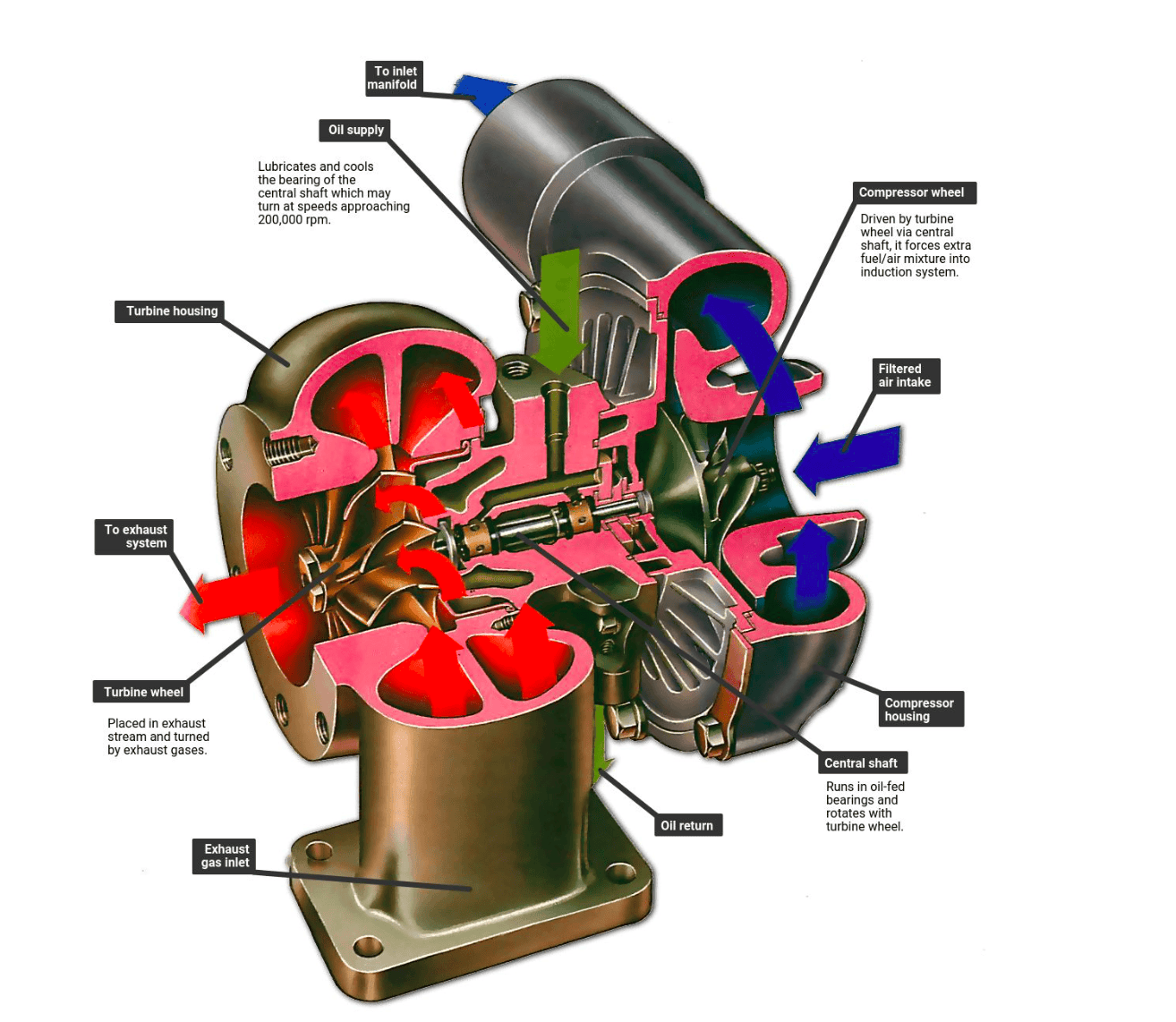
A turbocharger operates by utilizing the energy of the Exhaust Gases leaving the engine. It consists of two main parts: the Turbine Wheel and the Compressor Wheel. Both of these are mounted on a common shaft. The high-speed hot exhaust gases exiting the engine spin the turbine wheel. As a result, the connected compressor wheel also spins, forcing air into the engine at very high pressure. Turbine wheels can spin at incredibly high speeds, even up to 300,000 RPM.
Pros
The fuel efficiency of engines using this is very high. The reason is that since it reuses the energy of the exhaust gas, it is not a burden on the engine and provides greater efficiency. Therefore, it has the ability to produce large amounts of power from a small engine.
Cons
When considering the disadvantages, Turbo Lag is a significant drawback. It takes a small amount of time (a few milliseconds) for the exhaust gases to flow and bring the turbine up to the required speed. This delay is called 'Turbo Lag'. Twin-turbo technology is often used to minimize this lag. Also, since it operates on hot exhaust gases, the air heats up significantly. Therefore, almost every turbocharger system requires an Intercooler to cool the air.
Supercharger
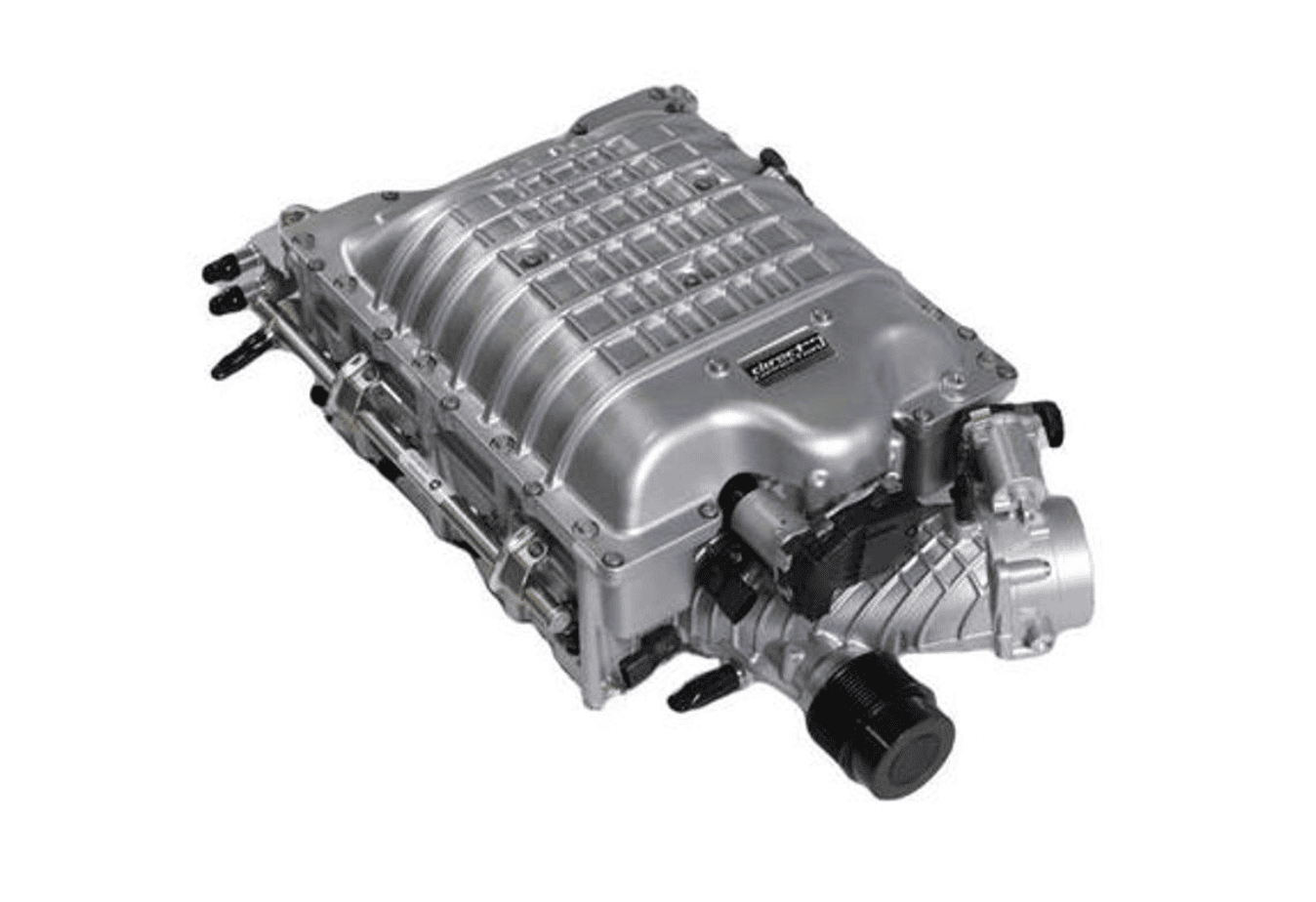

The supercharger is an older technology than the turbocharger. Its operation is somewhat simpler. A supercharger connects directly to the engine's Crankshaft via a belt and pulley. As the engine spins, the supercharger spins simultaneously, forcing air directly into the engine.
Superchargers can be identified mainly under two categories: Positive Displacement (Roots, Twin-Screw) and Dynamic (Centrifugal).
Positive Displacement Superchargers (Roots and Twin-Screw)
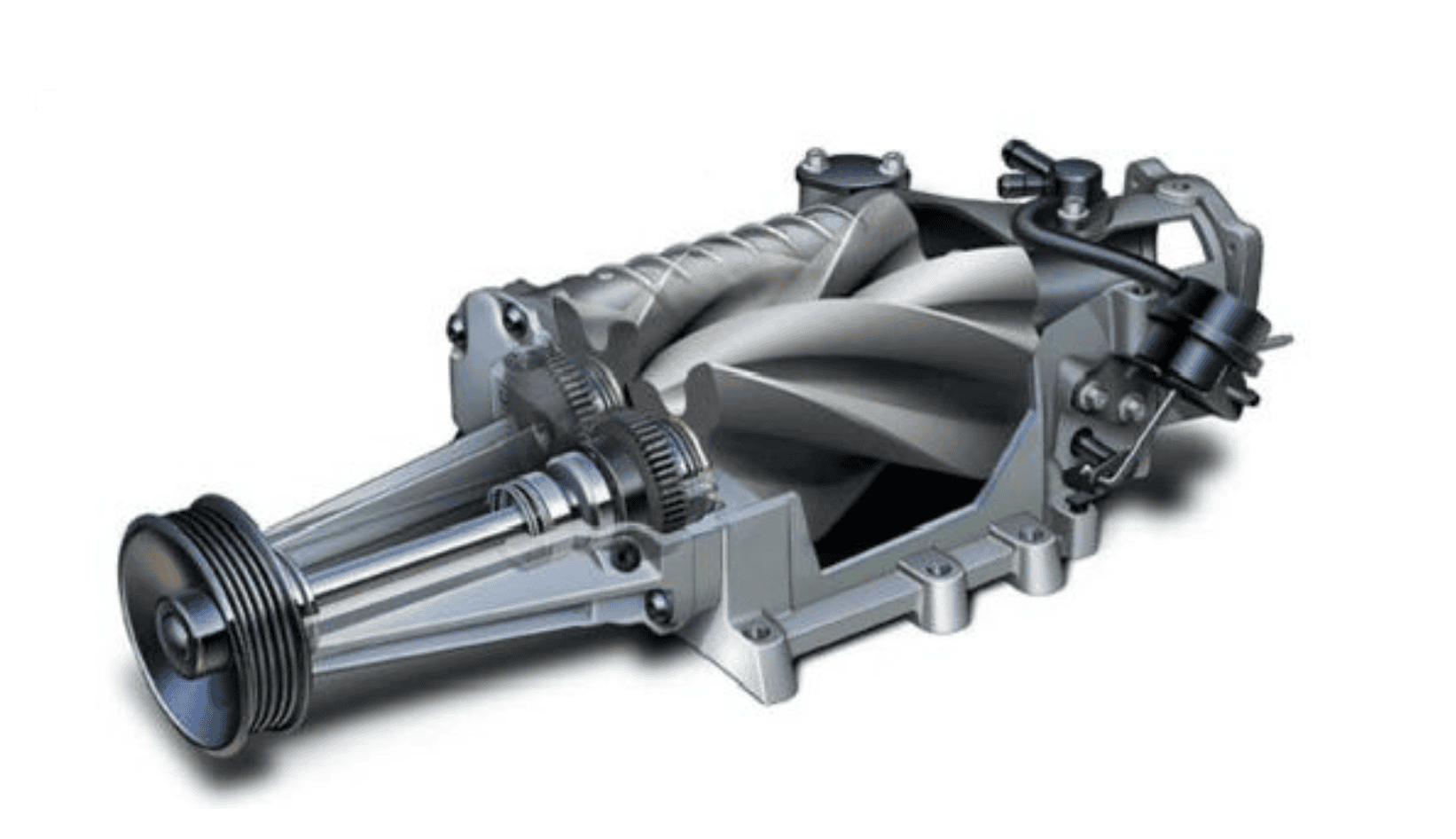
The specialty of this type of supercharger is that it keeps the air pressure (Boost Pressure) entering the engine as constant as possible, regardless of how low the engine speed (RPM) is. To explain how this works, it acts like a pump that "grabs" air and pushes it. With every revolution of the supercharger, a constant volume of air is sent to the engine. This means you feel a good 'boost' from the very beginning, even when the engine is running slowly.
- Roots Type: Has two lobed rotors connected to each other. As these rotors spin, they trap air and expel it into the engine.
- Twin-Screw Type: Made of two screw-shaped rotors. These take air, compress it inside the rotors (squeezing it into a smaller space), and send it to the engine. Therefore, they are more efficient than Roots.
Pros
Since pressure is available from the start, good torque is obtained at lower engine speeds (when starting the vehicle/moving slowly). This is great for daily driving and heavy vehicles. Also, you get boost the moment you touch the accelerator.
Cons
These generate a bit more heat when working, especially at high RPMs. Some Roots types create a bit more noise.
Dynamic (Centrifugal) Superchargers
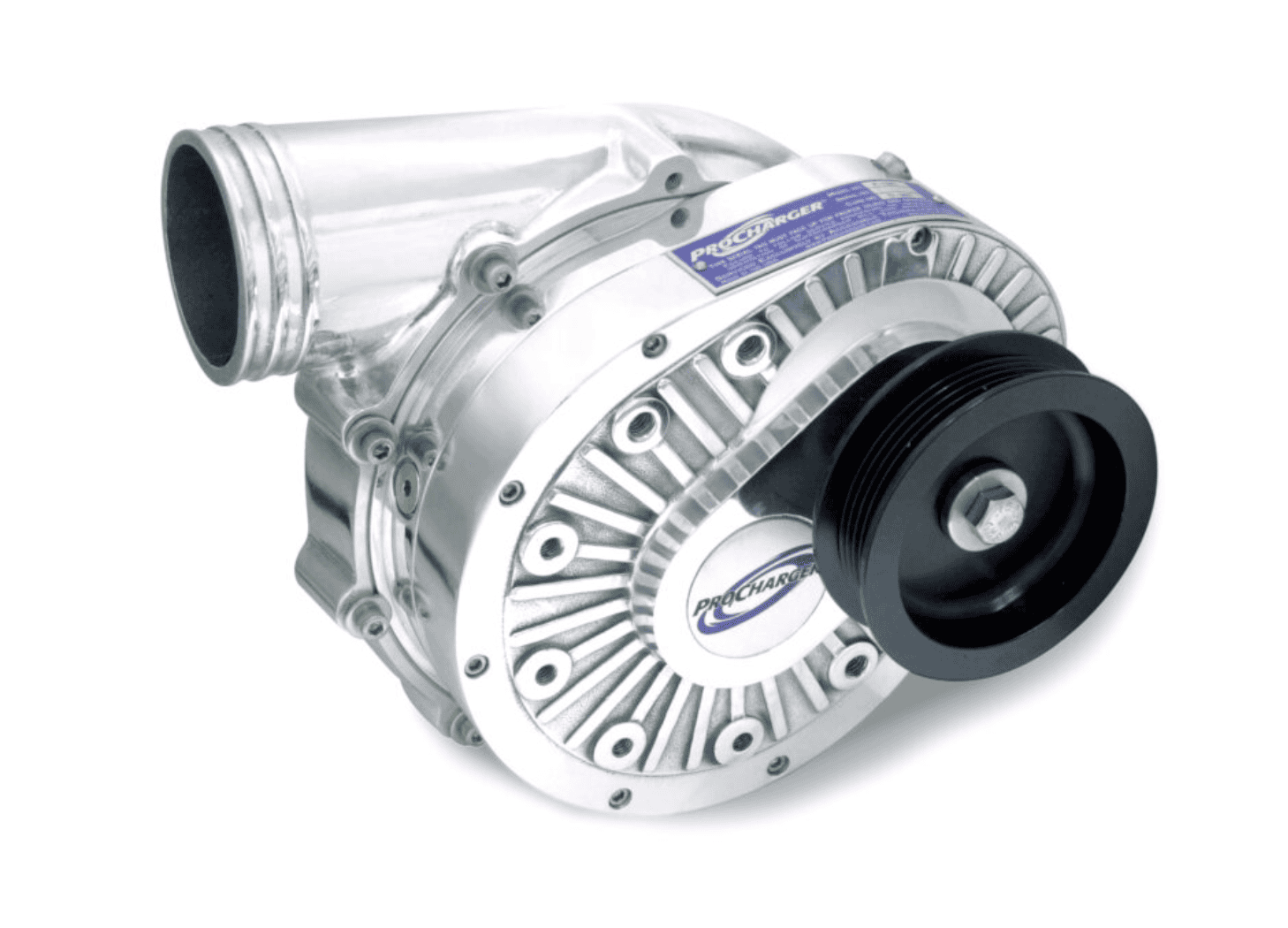
This type of supercharger works better as the engine speed (RPM) increases. The faster the engine runs, the more boost you get.
To explain how this works: These are very similar to the compressor of a turbocharger. It has a rapidly spinning Impeller. This impeller draws air in and pushes it out at high speed. Here, the spinning impeller gives Kinetic Energy to the air. Then, as it passes through a Diffuser, this speed is converted into pressure.
Pros
These work with very high efficiency at high engine speeds. Also, they produce less heat compared to the Positive Displacement type. Due to a simpler design than other types, they are generally easier to install.
Cons
When engine speed is low, the amount of boost drops rapidly. Therefore, you don't get huge torque/power initially. These are best suited for vehicles like racing cars that need High-End Power.
Overall Supercharger Pros & Cons
Pros
The advantage is the Instant Response. Since the supercharger operates directly off engine power, there is no 'Lag'. You get boost the moment you apply the accelerator. Also, because it is a simpler system than a turbocharger, installation is easier.
Cons
A major disadvantage is Parasitic Loss. The supercharger sucks a certain amount of power from the engine to operate. For example, if it requires 20 HP to run, even if it adds 40 HP, you effectively only get a Net Power of 20 HP. Also, fuel efficiency is lower compared to a turbocharger.
Conclusion
If you expect maximum efficiency and the greatest power, the Turbocharger is the best choice.
If you want an instant boost, zero delay, and clean power, especially in the low RPM range, choosing a Supercharger is suitable.
Today, some high-performance vehicles use both a Turbocharger and a Supercharger together (Twin-charging). The supercharger provides instant boost at low RPM, while the turbocharger kicks in at high RPM to provide maximum power.